C481 B581 Computer Graphics
Dana Vrajitoru
3D Representation and Modeling
Geometrical modeling
- Scalars, points, vectors
- Curves
- Surfaces
- Solid objects
Scalars, Points, Vectors
Scalar - a real number, a quantity.
Point - P(x, y, z), a location in space. 0-dimensional object in
the 3D space. In OpenGL a point can be drawn with
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
glVertexf(x, y, z); // as many as we need
glEnd();
Vector - V(x, y, z), a combination of a direction and a magnitude.
A vector does not have a fixed position in space. The usual representation
for some physical quantities like velocity, force.
Parametric Curves
Def. P(x(s), y(s), z(s)), a < s
< b. Usually a=0, b=1.
Notation: P(x(s), y(s), z(s)) = P(s).
1-dimensional object in the 3D space depending on one parameter s.
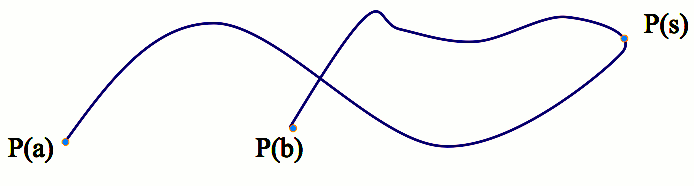
Examples:
| Line segment |
from (x1, y1, z1) to
(x2, y2, z2)
|
x(s) = (1-s) x1 + s x2
y(s) = (1-s) y1 + s y2
z(s) = (1-s) z1 + s z2
0 < s <
1 |
Circle in the Oxy plane
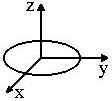
|
x 2 + y2 = r2
z=0 |
x(s) = r cos s
y(s) = r sin s
z(s) = 0
0 < s <
2 pi |
Spiral in the Oxy plane
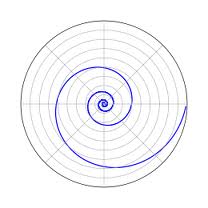
| General equation:
x2 + y2 = (r(s))2, z=0
|
x(s) = c s cos s
y(s) = c s sin s
z(s) = 0
0 < s < 5 pi
|
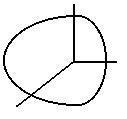
Helix
|
x 2 + z2 = r2
0 < y < 3 r |
x(s) = r cos s
y(s) = r s / (2 pi)
z(s) = r sin s
0 < s < 6 pi |
|
|
x(s) = 0
y(s) = (2 - cos s) cos s
z(s) = 2 sin s
0 < s <
2 pi |
Parametric Surfaces
Def. P(x(s, t), y(s, t), z(s, t)), a <
s < b, c <
t < d.
2-dimensional objects in the 3D space depending on two parameters s and t.
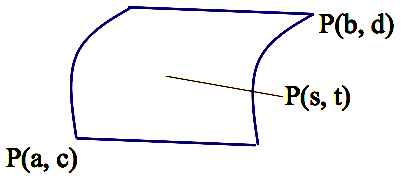
Examples:
Triangle
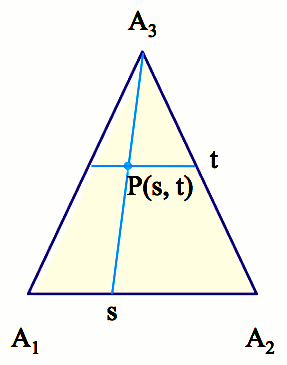
|
A1(x1, y1, z1) ,
A2(x2, y2, z2),
A3(x3, y3, z3) |
x(s, t) = (1-t)((1-s) x1 + s x2) + t x3
y(s, t) = (1-t)((1-s) y1 + s y2) + t y3
z(s, t) = (1-t)((1-s) z1 + s z2) + t z3
0 < s <
1, 0 < t <
1 |
Ellipsoid
|
(x/a) 2 + (y/b)2 + (z/c)2 = 1 |
x(s) = a cos s cos t
y(s) = b sin s cos t
z(s) = c sin t
0 < s <
2 pi, 0 < t < 2 pi |
Cylinder
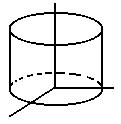
|
x 2 + y2 = r2
0 < z <
a |
x(s, t) = r cos s
y(s, t) = r sin s
z(s, t) = t
0 < s <
2 pi, 0 < t < a |
Cone
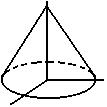
|
x 2 + y2 = (1 - z)2
0 < z <
1 |
x(s, t) = (1 - t) cos s
y(s, t) = (1 - t) sin s
z(s, t) = t
0 < s <
2 pi, 0 < t < 1 |
Rotation surface
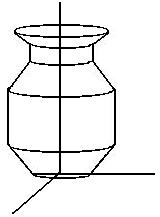
|
Given a planar curve
(x1, y1)
construct the rotation
surface around 0y:
x 2 + z2 =
x12
y = y1
|
(x1(s), y1(s))
x(s, t) = x1(s) cos t
y(s, t) = y1(s)
z(s, t) = x1(s) sin t
|
Solid objects
Def. P(x(s, t, u), y(s, t, u), z(s, t, u)), a <
s < b, c <
t < d, e <
u < f;
3-dimensional objects in the 3D space depending on three parameters s, t,
and u;
In CG they are represented by the bounding surface which is closed.
Sometimes we need to visualize the whole volume, like for medical images.
Discretization
- The 3D equivalent of scan converting from the 2D.
- For a curve: starting from the general continuous
parameterization, representing the curve as a sequence of (small) line
segments.
- For a surface: starting with the general continuous
parameterization, representing the surface as a collection of
polygons, usually triangles or quadrilaterals.
- A volume is usually discretized as a collection of units of volume
(voxels) represented as points, spheres, cubes, etc.
Discretizing curves.
Consider the curve x(s), y(s), z(s), a <
s < b.
We want to draw the curve as a number of nlines line segments.
step = (b - a) / nlines;
for (i=0; i<nlines; i++) {
s1 = a + i * step;
s2 = a + (i+1) * step;
Line3D(x(s1), y(s1), z(s1),
x(s2), y(s2), z(s2));
}
In OpenGL: represent the curve as a line strip.
step = (b - a) / nlines;
glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
for (i=0; i<=nlines; i++) {
s = a + i * step;
glVertex3f((x(s), y(s), z(s));
}
glEnd();
Discretizing surfaces.
Consider the surface x(s, t), y(s, t), z(s, t), a <
s < b, c <
t < d.
We want to discretize it using spoints along s and tpoints
along t.
point(s, t) : x(s, t), y(s, t), z(s, t).
sstep = (b - a) / spoints;
tstep = (d - c) / tpoints;
for (i=0; i<spoints; i++) {
s1 = a + i * sstep;
s2 = a + (i+1) * sstep;
for (j=0; j<tpoints; j++) {
t1 = c + j * tstep;
t2 = c + (j+1) * tstep;
// First model
Polygon(point(s1, t1),
point(s1, t2),
point(s2, t2), point(s2, t1),
point(s1, t1));
// Second model
Triangle(point(s1, t1),
point(s1, t2), point(s2, t1));
Triangle(point(s1, t2),
point(s2, t1), point(s2, t2));
}
If the triangle or the polygon is drawn as a collection of lines, we have
wireframe models.
In OpenGL: represent each band in the surface for given s1 and s2
as a triangle strip.
sstep = (b - a) / spoints;
tstep = (d - c) / tpoints;
for (i=0; i<spoints; i++) {
s1 = a + i * sstep;
s2 = a + (i+1) * sstep;
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP);
for (j=0; j<=tpoints; j++) {
t = c + j * tstep;
glVertex3f(x(s1,t), y(s1,t),
z(s1,t));
glVertex3f(x(s2,t), y(s2,t),
z(s2,t));
}
glEnd();
}










