Models Inspired from Operating Systems
Some parallel programming schemes inspired from tasks that can be a part of an operating system.
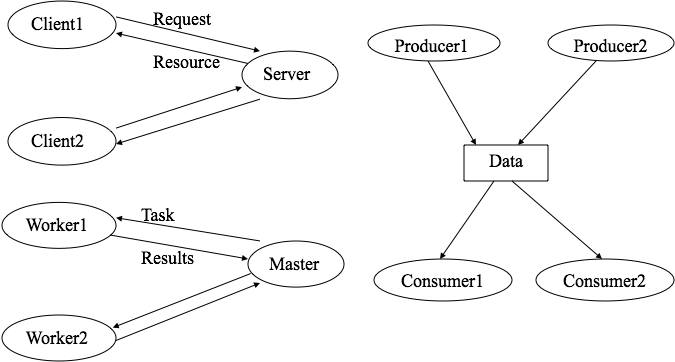
Client-Server
A model that is similar to the previous one, only the roles of the
master-workers are exchanged. This time the master is a server that
can perform tasks or provide some information, or give access to some
resources. The slave processes are the clients that send in requests
for service.
Client-Server in General
Benefits of the System
Architectures
Client Types
Server Types
Client-server Implementation
The simple model: the server receives a request and processes
it right away.
Server() {
while (true) {
Recv(request, any_source);
client = source;
result = Process(request);
Send(result, client);
}
}
Client() {
while (true) {
request = Generate_request();
Send(request, server);
Recv(result, server);
Process_result(result);
}
}
A more complex model: using a queue of requests.
Server() {
Queue clientq, requestq;
Initiate_receive(request, any_source); // non-blocking
while (true) {
choose randomly between
Process_request(clientq, requestq);
Get_request(clientq, requestq, request);
}
Process_request(clientq, requestq) {
if (!requestq.is_empty()) {
request = requestq.dequeue();
client = clientq.dequeue();
result = Process(request);
Send(result, client);
}
}
Get_request(clientq, requestq, request) {
if (Received(request)){
client = source;
clientq.enqueue(client);
requestq.enqueue(request);
Initiate_receive(request, any_source);
}
}
In a more complex model, we could sort the tasks by order of priority in the queue. To avoid a deadlock, the priority of any task in the queue should increase with time.
Peer to Peer Systems